Twin Towers
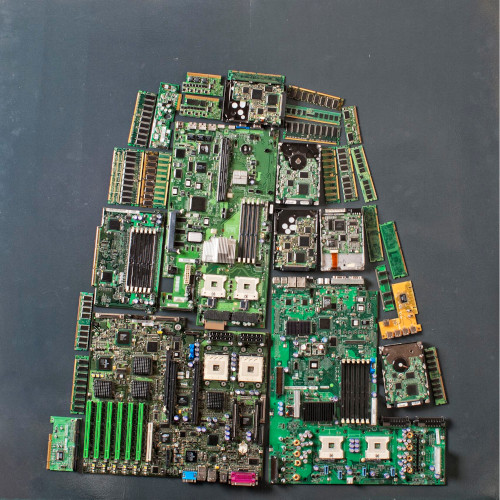
Upcycling obsolete computer parts into priceless abstracts.

Upcycling obsolete computer parts into priceless abstracts.
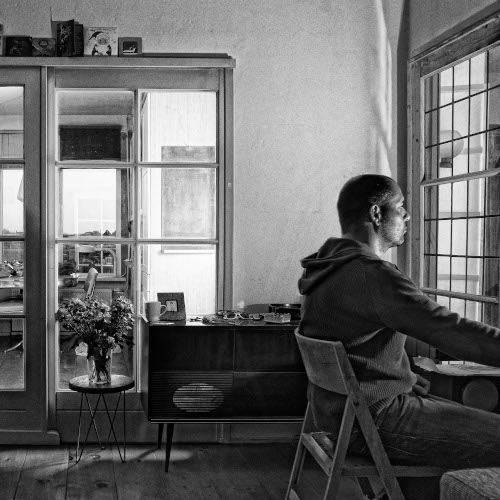

Portrait series of people working at home at the computer.
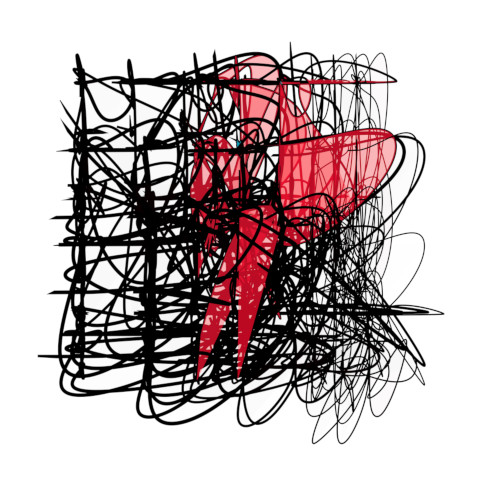

Generative or algorithmic art project in C# started in 2008. Developed a couple of versions over the years until a final version 7. Currently switched over to p5.js as a language in the Sakura project.
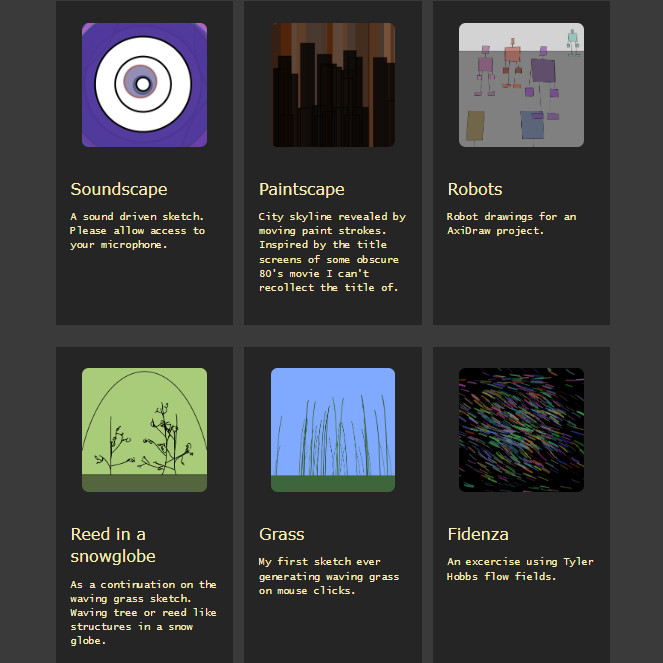
Continuation of the concept of the Helena project as in 'Computers creating art' using the p5.js framework and integration with an AxiDraw plotter.
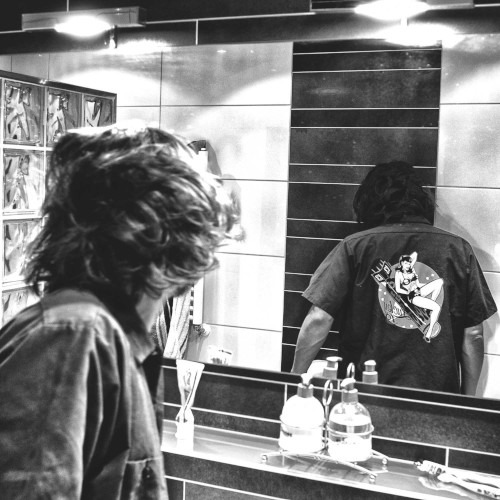

Creating is cool.
Selling art is decadent.
Buying art is decadent.
Exhibiting is cool.
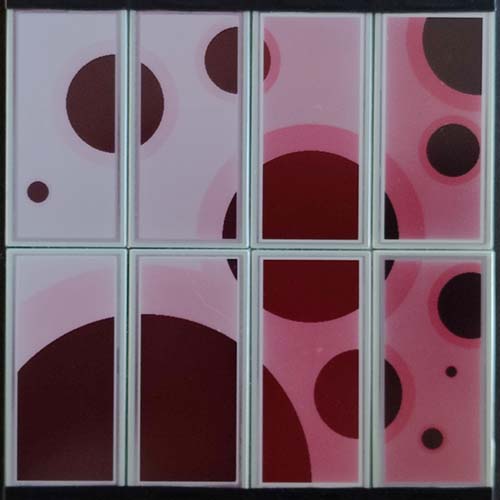

An Electronic Paper Display (EPD) has a programmable interface with wich shapes can be drawn in a two dimensional plane defined with an x- and y-axis.
You need electricity, a computer and some programming logic to create the image but once the image is created the EPD can retain there image without electrical power indefinitely.
-- What do you see when you're looking into the eyes of a madman, on the verge of insanity?
Looking out the window I see the animals in the darkness, the fearless, the scandalous, the heartless.
The psycho realm - Temporary insanity
Jeroen Vesseur, Schiedam, The Netherlands, 2023